The Critical Role of Cold Chain in Vaccine Efficacy
Vaccines have long been a powerful tool in public health, saving millions of lives each year from infectious diseases. From childhood immunizations to emergency rollouts during pandemics, vaccines are key to global health progress. However, maintaining the right temperature throughout the supply chain is crucial to preserving their effectiveness. Even small temperature changes can reduce a vaccine's effectiveness or make it unsafe. This is where cold chain management is vital.
A strong cold chain system ensures vaccines stay within the required temperature range from production to administration. It involves coordinated processes like refrigeration, transportation, and storage. With the global complexity of vaccine distribution, especially for mRNA vaccines that need ultra-cold storage, effective cold chain management is more important than ever.
Understanding the impact of temperature on vaccines, the cold chain components, and technological advances in this area is crucial to maintaining vaccine safety and efficacy. Healthcare workers, logistics teams, and policymakers need to use this knowledge to manage the cold chain properly.
Understanding the Science of Vaccine Cold Chains
Vaccines are sensitive biological products with active ingredients that trigger immune responses. Many components, like proteins and nucleic acids, break down when exposed to temperatures outside the recommended range. Excessive heat can damage a vaccine’s molecular structure, reducing its effectiveness. Freezing vaccines with aluminum-based adjuvants can cause irreversible damage, making them ineffective.
Temperature requirements vary by vaccine type. Live vaccines (e.g., measles, yellow fever) are stored in refrigerators at 2°C to 8°C, while inactivated vaccines (e.g., influenza, hepatitis B) also require similar conditions. mRNA vaccines (e.g., COVID-19 vaccines) need ultra-low temperatures of -70°C, requiring special measures for stability.
Stability testing helps determine the correct temperature management standards for vaccines. Pharmaceutical companies conduct research to identify the conditions needed to preserve vaccine efficacy.
These findings are shared with regulatory agencies like the WHO and CDC to create guidelines for vaccine storage and transport.
Key Components of Vaccine Cold Chains
Maintaining vaccine efficacy requires a cold chain system that spans multiple stages, each with unique challenges. Strict adherence to optimal management practices is essential at each stage.
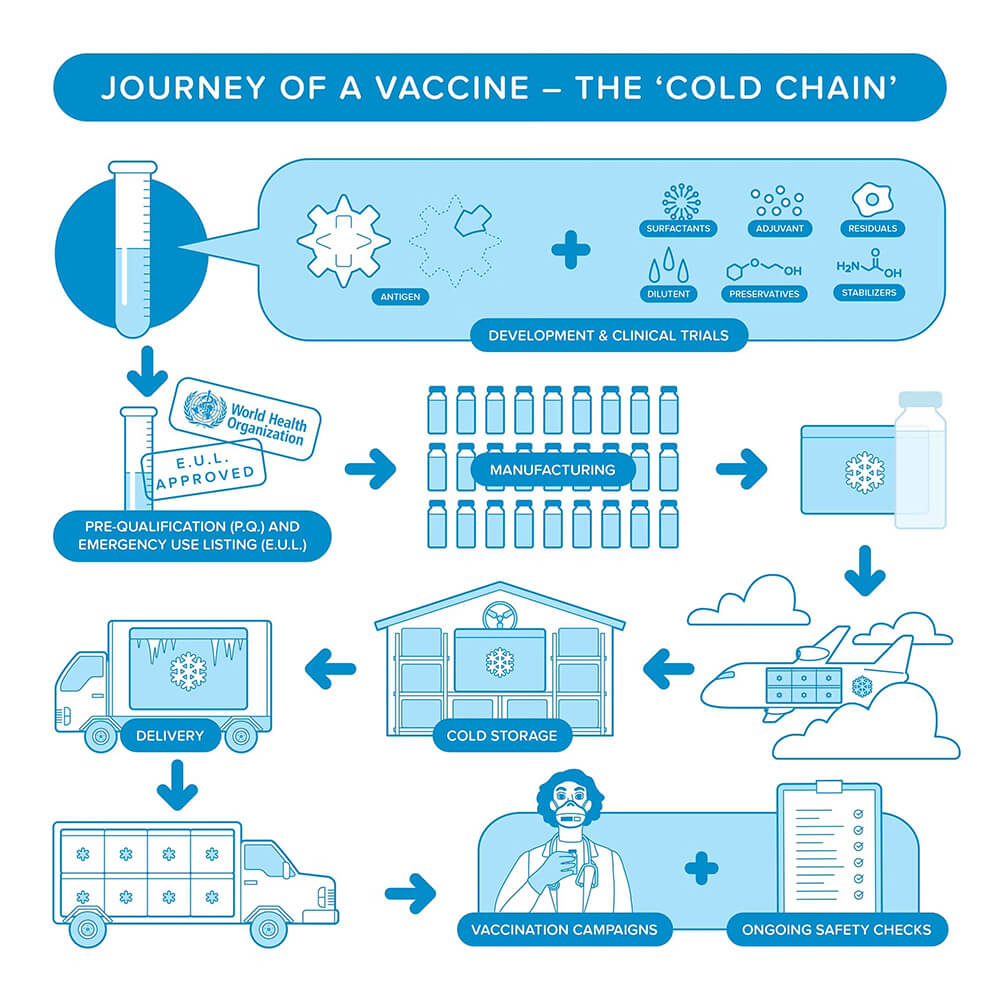
Source: Pan American Health Organization.
1. Manufacturing and Initial Storage
The manufacturing and initial storage phase is a critical foundation for the cold chain. From the moment vaccines leave the production facility, they must be stored at carefully controlled temperatures. Dedicated low-temperature storage facilities are equipped with specialized cooling systems that ensure the vaccines remain stable until they are ready for shipment.
2. Transportation
Transportation is another key stage. Whether vaccines are shipped internationally or distributed locally, keeping the right temperature is essential. Cold chain logistics involve refrigerated trucks, temperature-controlled containers, and packaging that protects against temperature changes. Data loggers and temperature sensors monitor conditions in real-time during transport.
3. Storage at Destination
Once vaccines reach their destination, the storage facility plays a key role in preserving their quality. Hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies need the following medical-grade equipment:
- Medical refrigerators
- Ultra-low freezers (especially for mRNA vaccines)
- Backup power systems in case of power outages
Vaccines should be stored in designated temperature-controlled areas, and frequent door openings or exposure to external environments should be minimized to maintain stability.
4. Final Delivery and Administration
Temperature control must be maintained during final delivery and vaccine administration. Healthcare providers should be trained in vaccine storage and preparation to ensure they administer vaccines effectively. In remote or mobile vaccination clinics, portable low-temperature storage equipment is crucial for proper vaccine management.
Maintaining an Effective Vaccine Cold Chain
Healthcare professionals and logistics personnel must follow best practices to maintain vaccine efficacy throughout the supply chain. Temperature monitoring and documentation are key. Using digital tools like remote sensors and cloud-based tracking systems provides real-time data, allowing quick action if temperatures fall outside the acceptable range.
Emergency Preparedness is Also Crucial
Power outages, equipment malfunctions, or unexpected delays can jeopardize the cold chain. Ensuring backup power sources, such as generators, and developing emergency response plans are essential to safeguard vaccines. Additionally, training healthcare providers on proper handling and storage protocols can reduce human errors that lead to vaccine wastage and strengthen the system overall.
Key Role of Compliance in Cold Chain Management
International guidelines established by the WHO, CDC, and national health authorities outline the necessary vaccine storage and distribution procedures. Adhering to these standards preserves vaccine efficacy and helps build public trust in vaccination programs.
Challenges and Solutions in Vaccine Cold Chains
Vaccine cold chain management faces several challenges. Global disruptions, like pandemics or geopolitical conflicts, can cause delays in vaccine distribution. Strong international cooperation and emergency response plans are needed to address these issues and ensure vaccines reach their destinations quickly.
In resource-limited areas, poor infrastructure adds more obstacles. Many places lack reliable power or refrigerated storage, making it hard to maintain the cold chain. Portable vaccine carriers with phase-change materials provide an effective mobile refrigeration solution.
Additionally, ensuring fair vaccine distribution brings both ethical and logistical challenges. Priority must be given to areas with the greatest need, while considering logistical feasibility. Transparent distribution strategies and investments in cold chain infrastructure can help reduce gaps between high-income and low-income countries.
Key Takeaways: Securing Vaccine Integrity
Maintaining a strong vaccine cold chain is a shared responsibility that requires collaboration among governments, healthcare organizations, and logistics providers. Following best practices, using new technologies, and addressing infrastructure challenges are key to ensuring vaccines stay effective from production to administration. Strengthening cold chain management helps protect lives and reduce global health disparities.
A critical part of this system is reliable refrigeration. Facilities handling temperature-sensitive products, such as vaccines and blood, benefit from PHCbi’s blood bank refrigerators, which offer precise temperature control and uniform cooling. These refrigerators keep vaccines within the proper 2°C to 8°C range and feature forced air cooling systems and real-time temperature monitoring to maintain quality in difficult conditions. For more details on PHCbi's blood bank refrigerators and their role in vaccine storage, visit the product page.
To safeguard future generations, continued investment in resilient and efficient vaccine supply chains is essential.